Introduction
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) is a way of looking at organisational change which focuses on identifying and doing more of what is already working, rather than looking for problems and trying to fix them. It makes rapid strategic change possible by focusing on the core strengths of an organisation and then using those strengths to reshape the future.
AI is a participative learning process to identify and spread best practice. It is also a way of managing and working that encourages trust, reduces defensiveness and suspicion, and helps to establish strong working relationships quickly.
Why is the topic important:
The key feature of this approach is that it uses existing strengths, achievements and successes – the aspects of people’s work that they are proud of, that motivate them, and that are getting good results – as a foundation for a credible vision of the future, and a launching pad to reach that future vision. It does not ignore past failures but helps people to collectively get into a more positive and therefore more creative frame of mind to come up with ideas for improvement.
The very act of asking a question influences the state of mind of the person who is asked. Because teams, organisations and societies move toward what they persistently ask questions about, an Appreciative Inquiry is the investigation of those things that are most effective within an organisation or any other sort of human system.
Once we have identified this “positive core” and linked it directly to a strategic agenda, changes not previously thought possible can be rapidly achieved while at the same time building enthusiasm, confidence and energy to get things done.
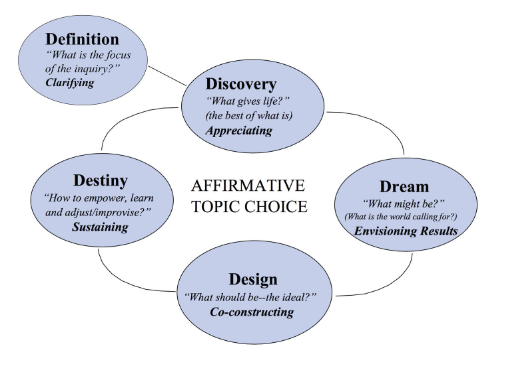
Summary of the key methods:
Comparison with Problem focused approaches
|
Problem-solving |
Appreciative Inquiry |
|
What to fix |
What to grow |
|
Thinks in terms of problem, symptoms, causes, solutions, action plan, intervention, and all too often, blame |
Thinks in terms of good, better, possible. |
|
Breaks things into pieces, leading to fragmented responses |
AI keeps the big picture in view, focusing on an ideal and how its roots lie in what is already working |
|
Slow pace of change – requiring a lot of positive emotion to make real change |
Quickly creates a new dynamic – with people united around a shared vision of the future |
|
Assumes an organisation is made up of a series of problems to be overcome, creating a deficit culture |
Assumes an organisation is a source of limitless capacity and imagination, creating an appreciative culture |
Challenge
Objective: To identify and amplify what works well within a team or organisation.
Step 1: Discover (30 minutes)
Pair Up: Form pairs within your group.
Positive Experience Sharing: Each person takes turns to share a story about a peak experience they had while working in the team/organisation. This could be a time when they felt exceptionally engaged, proud, or when the team achieved something significant.
Here are some guiding questions:
- What was the situation?
- What made it a positive experience?
- What did you do that contributed to the success?
- How did others contribute?
Step 2: Dream (30 minutes)
Reflect: Each pair reflects on the stories shared and identifies common themes, strengths, and factors that contributed to these positive experiences.
Envision the Future:
- Imagine the team/organisation is functioning at its best in the future. Discuss and visualise what that would look like.
- What are the core values and strengths that are being utilised?
- What new possibilities and opportunities can be created by building on these strengths?
Step 3: Share and Discuss (30 minutes)
Group Sharing: Each pair shares the key insights from their discussions with the larger group.
Collective Themes: As a group, identify and note down recurring themes, strengths, and visions for the future.
This activity will help participants understand the core principles of Appreciative Inquiry by focusing on positive experiences and envisioning a future that leverages their strengths.
Summary of Material:
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) is a method for creating positive change in organisations by focusing on what works well, rather than fixing problems. It involves discovering strengths and envisioning a future that builds on these strengths.
The benefits of using AI include:
- Uses validated successes and accomplishments to inspire
- Enhances participation, cooperation and leadership
- Helps reach a consensus
- Implements problem-solving from a strengths-based perspective
- Shifts the focus from the negative to the positive, from weaknesses to strengths
